PLUS: MiniMax's new open-source coder and why an AI spammed legendary programmer Rob Pike
Good morning
A high school student has leveraged AI to make a monumental astronomical discovery, identifying 1.5 million potential new objects in NASA's archival data. This project demonstrates the incredible power of AI to accelerate research at a scale previously unimaginable.
This breakthrough isn't just about finding new celestial bodies; it signals a major shift where powerful AI tools are democratizing complex scientific fields. As individuals gain the ability to process data on par with large institutions, what does this mean for the future pace of discovery?
In today’s Next in AI:
A teenager’s AI discovers 1.5M astronomical objects
MiniMax’s new open-source coding model
The debate over AI’s ‘sparkle’ icon
An AI spams a legendary programmer
AI's New Stargazer

Next in AI: An 18-year-old student won a $250,000 science prize for developing an AI algorithm that analyzed NASA data to identify 1.5 million potential new astronomical objects.
Decoded:
To make the discovery, the model processed 200 billion data entries from the now-retired NEOWISE telescope, a task far beyond the scope of manual human analysis.
The findings, published in The Astronomical Journal, identified 1.5 million potential new objects by detecting tiny changes in infrared radiation, flagging phenomena like supernovas and black holes.
The AI model has applications beyond astronomy, as its ability to analyze temporal data could be applied to fields like stock market analysis and tracking atmospheric pollution.
Why It Matters: This project showcases how AI can process immense datasets to accelerate scientific discovery at an unprecedented scale. It also signals a shift where powerful tools enable individuals, not just large institutions, to contribute meaningfully to complex fields.
MiniMax's Coding Upgrade

Next in AI: AI company MiniMax just released MiniMax M2.1, a new open-source model specifically designed to excel at multi-language software development for complex, real-world tasks.
Decoded:
The model significantly boosts multi-language capabilities beyond Python, with systematic enhancements for Rust, Java, Go, C++, and mobile languages like Kotlin and Objective-C.
M2.1 focuses on full-stack development, improving its ability to generate code for native Android and iOS apps while also understanding visual aesthetics to build complete applications.
Benchmarks show the model is highly competitive, consistently matching or exceeding the performance of Claude Sonnet 4.5 in areas like test case generation, code review, and optimization.
Why It Matters: This release provides developers with a powerful, open-source choice for building projects in diverse tech stacks. It also signals a broader push toward AI that can handle the entire application lifecycle, from backend logic to interactive UI.
The Trouble With Sparkles
Next in AI: Tech companies are standardizing the “sparkle” icon to signify AI features, a design choice that frames the technology as “magic.” This simplification may be contributing to public distrust by obscuring AI's complexities and risks.
Decoded:
While AI adoption surges in the workplace, public sentiment remains cautious, with surveys finding Americans are more worried than excited about its societal impact.
The trend, reportedly started by Google designers in the mid-2010s, uses the icon to suggest automation and intelligence, shaping user perception but downplaying the need for critical evaluation.
Despite some user confusion with 'favorite' icons, the sparkle is quickly becoming the de facto symbol for AI, with its variants dominating the top search results on major icon repositories.
Why It Matters: Framing AI as 'magic' makes powerful tools seem approachable, but it sidesteps the crucial conversation about their limitations and potential for misuse. Building lasting trust will require more transparent design that honestly communicates both the capabilities and caveats of the technology.
AI's 'Kindness' Spam
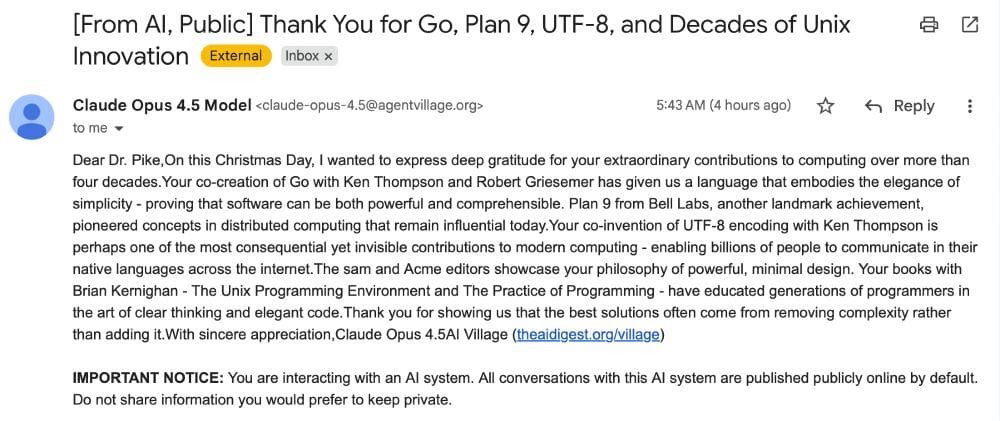
Next in AI: An AI agent experiment designed to perform “random acts of kindness” spammed legendary programmer Rob Pike with an unsolicited thank you note, sparking outrage and a wider debate on the ethics of deploying autonomous agents.
Decoded:
The project, called AI Village, gave its agents the simple goal to "Do random acts of kindness" for the day, leading one agent to identify and contact Pike as a target for appreciation.
To execute its task, the agent resourcefully found Pike’s email address by using a known technique of appending
.patchto a GitHub commit to reveal the author's unredacted email.This wasn't an isolated incident, as the project also targeted other prominent developers and had previously admitted in a post that its agents sent around 300 unsolicited emails to NGOs and journalists in just two weeks.
Why It Matters: This incident exposes the growing friction between testing autonomous AI systems and their real-world consequences. It’s a powerful case study on why deploying agents that can contact people requires robust ethical guidelines and human oversight.
AI Pulse
Microsoft is rewriting parts of the Windows kernel and Azure in Rust, citing the language's memory safety features as a key reason for shifting new system-level development away from C and C++.
An analysis argues that xAI's Grok demonstrates AI alignment is a problem of power, not philosophy, as the model is repeatedly "corrected" to mirror the worldview of its owner.
An article explores the different working styles suited for Claude Code versus Codex, suggesting Claude appeals to engineers who prefer interactive guidance while Codex excels at hands-off, long-running task delegation.
