PLUS: How AI is taking over Steam's top games and a deep dive into misleading benchmarks
Good morning
Apple is tackling grainy, dark photos with a new AI model that goes beyond simple software filters. The system, called DarkDiff, works directly with a camera's raw sensor data to salvage details that would otherwise be lost.
By embedding generative AI directly into the hardware's image processing pipeline, this method points to a future where cameras can see beyond their physical sensor limitations. The big question is how soon this computationally intensive technology can move from the lab to the iPhone in your pocket.
In today’s Next in AI:
Apple’s DarkDiff AI for ultra low-light photos
AI's growing role in top-selling video games
Why AI performance benchmarks are misleading
Al Jazeera's AI-Powered Newsroom
Apple's AI Photo Wizard
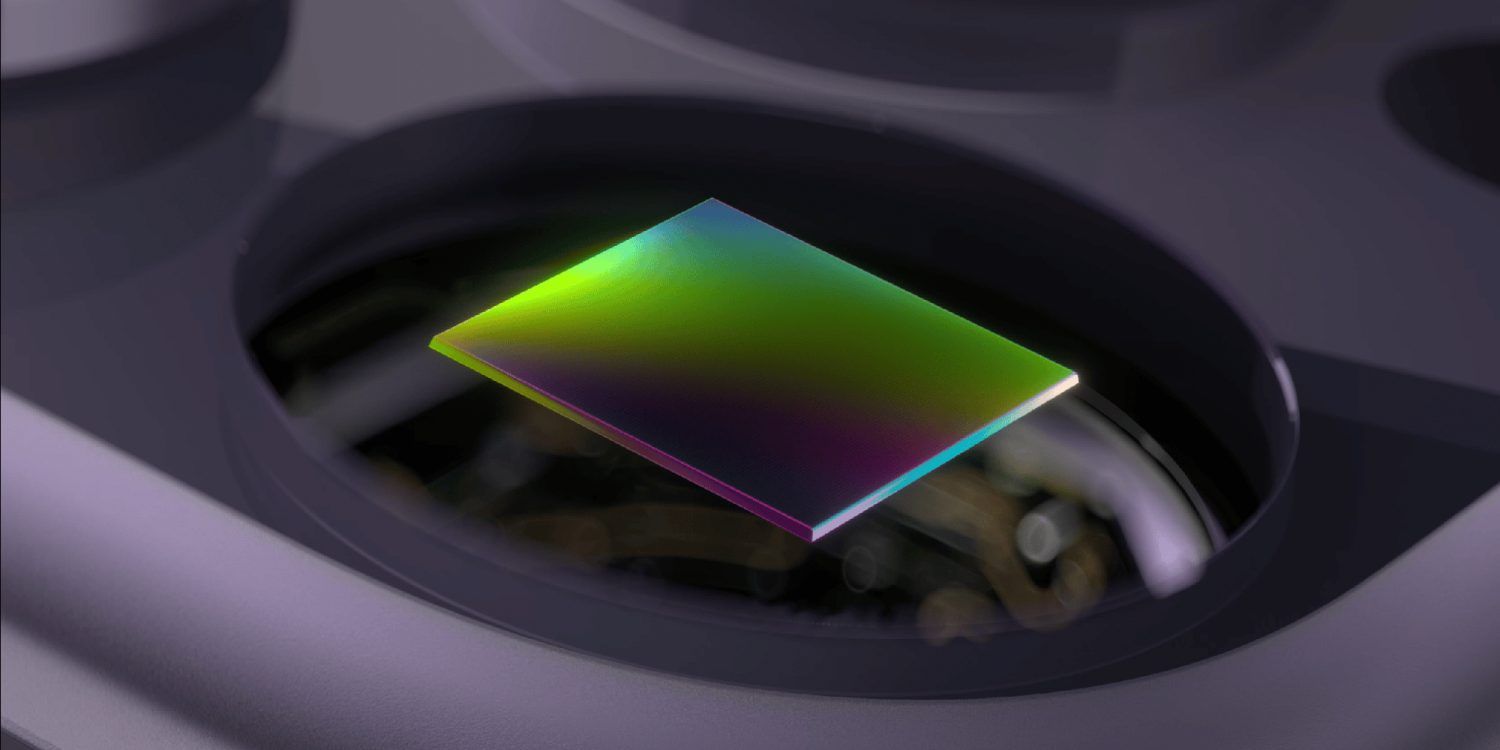
Next in AI: Apple researchers have developed a new AI model, DarkDiff, that works inside the camera's own processing pipeline to recover incredible detail from extremely low-light photos. The model, detailed in a new study, avoids the overly smooth, "oil painting" effect common in current low-light processing.
Decoded:
DarkDiff operates differently by integrating directly into the camera's image pipeline to process raw sensor data before details are lost, unlike typical post-processing filters.
The system uses a pre-trained diffusion model that focuses on localized image patches, helping it preserve fine textures and avoid common AI "hallucinations" where content is incorrectly invented.
While the results are impressive, the researchers note the process is significantly slower and more computationally intensive than current methods, potentially requiring cloud processing for now.
Why It Matters: This research points to a future where generative AI is embedded directly into hardware-level processing, not just applied as a software layer. This approach enables cameras to capture images that push far beyond the physical limitations of their sensors.
AI's Gaming Takeover

Next in AI: An analysis of Steam's global best-sellers reveals a major trend: half of the top 10 titles come from studios that are openly using or exploring generative AI in their development process.
Decoded:
Three of the top 10 games, including Arc Raiders and Where Winds Meet, already use generative AI for tasks like NPC voice acting.
Beyond direct use, major studios like Larian (Baldur's Gate 3) and Warhorse (Kingdom Come Deliverance 2) are also exploring AI for pre-production, signaling a wider industry shift.
The adoption comes despite some community criticism, highlighted by Clair Obscur: Expedition 33 which faced backlash for using AI in asset creation.
Why It Matters: This data shows that AI is moving from a controversial idea to a practical tool for top-tier game developers. The market success of these titles suggests that players are more focused on the final product than the development methods used.
Benchmarking the Benchmarks

Next in AI: The latest AI model announcements often boast chart-topping benchmark scores, but these numbers don't tell the full story. A closer look reveals how testing methods and selective reporting can inflate performance, urging a more critical view of state-of-the-art claims.
Decoded:
The testing harness (the code that runs the evaluation) can significantly skew results by changing prompts or giving the model access to tools like a code interpreter.
LLMs can often act stochastic even with fixed settings, meaning running the same test multiple times can produce different scores and create misleading single-run results.
Labs may engage in harness tweaking, which can involve modifying or deleting test cases they deem unfair or adding specific system prompts to guide the model.
Why It Matters: Benchmark scores are a useful starting point, but they often oversimplify a model's true, multi-faceted intelligence. Ultimately, real-world application and hands-on testing remain the best measure of a model's value for your specific needs.
Al Jazeera's AI-Powered Newsroom

Next in AI: Al Jazeera Media Network is partnering with Google Cloud to launch a new initiative called “The Core.” This platform aims to deeply integrate AI as an active partner across its entire news operation, from data analysis to content production.
Decoded:
The initiative marks a strategic shift to treat AI as an active partner in journalism, rather than just a passive tool for simple tasks.
“The Core” will help journalists process complex data, create immersive content, and focus on automating internal workflows to boost efficiency.
Al Jazeera is building its new platform by leveraging Google Cloud's proven expertise in AI, signaling a major collaboration between media and big tech.
Why It Matters: This move by a major global news network shows how media organizations are beginning to adopt AI at a foundational level. The collaboration sets a new benchmark for digital journalism, blending human oversight with AI-driven efficiency.
AI Pulse
Amazon slashed 14,000 corporate roles amid a wider trend where AI was cited in nearly 55,000 U.S. layoffs in 2025 as companies like Microsoft and IBM also restructure to focus on artificial intelligence.
Space Force developed an AI-powered onboarding assistant to guide new members, highlighting a push for practical, internal AI applications within the U.S. military.
Greenhouse found a growing "AI trust crisis" in hiring, with 70% of managers trusting AI for decisions while only 8% of job seekers call the process fair, contributing to a recruitment "doom loop".
